1.1. 개요
iptables 는 Packet Filtering (Netfilter) 도구로써 방화벽 구성을 하기 위한 주요 기능을 제공합니다.
iptables 명령어의 기본 사용법은 크게 요약하면 다음과 같은 명령행 옵션들로 구분할 수 있습니다.
본 문서는 개인적인 해석 관점에 의해서 작성되었으며 모든 내용을 담고 있지 않습니다. 참고로만 봐주시고 보다 자세한 내용은![[http]](https://www.minzkn.com:443/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) netfilter 홈페이지
netfilter 홈페이지![[]](/moniwiki/imgs/moni2/external.png) (http://www.netfilter.org/)를 참고하세요.
(http://www.netfilter.org/)를 참고하세요.
iptables 명령어의 기본 사용법은 크게 요약하면 다음과 같은 명령행 옵션들로 구분할 수 있습니다.
$ iptables [-t <table>] [<action>] [<chain>] [<match>] [-j <target>]
본 문서는 개인적인 해석 관점에 의해서 작성되었으며 모든 내용을 담고 있지 않습니다. 참고로만 봐주시고 보다 자세한 내용은
![[http]](https://www.minzkn.com:443/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) netfilter 홈페이지
netfilter 홈페이지![[]](/moniwiki/imgs/moni2/external.png) (http://www.netfilter.org/)를 참고하세요.
(http://www.netfilter.org/)를 참고하세요.
1.1.1. 기본적으로 이해해야 하는 것들
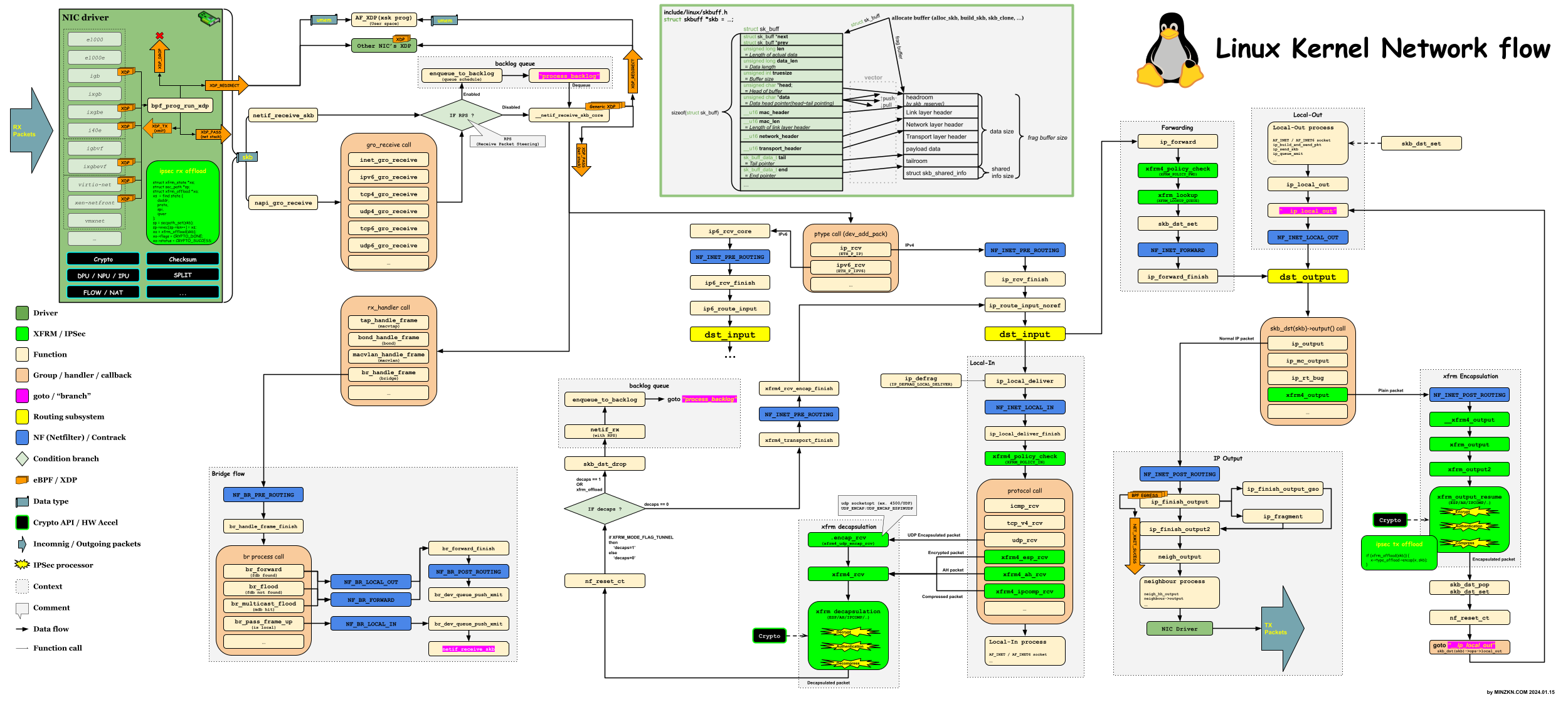
[PNG image (443.03 KB)]
- 체인(Chain) : 위 그림에서 Kernel내에서 packet의 흐름에 있어서 'NF_XXX' 으로 표시되는 파란색부분을 기점으로 하는 것 (노란색부분은 라우팅 기점으로 dst_input 에서 Local-In 또는 Forward를 결정하게 되며 dst_output 은 Forward 또는 Local-Out 을 거쳐서 최종 Output을 결정하게 됨.)
'PREROUTING': pre-routing- 패킷이 인입되는 초입부
- 위 그림에서 NF_XXX_PRE_ROUTING 으로 표시된 부분
- DEV-NOTE: Linux Kernel source 상에서 보면 통상적으로 IPv4 기준인 경우에는 ip_route_input 함수 호출하기 이전을 의미함.
- ip_route_input_XXX를 호출한 직후 dst_input의 경로(Local-In/Tunnel-Decapsulation 또는 Forward 를 결정하는 것)가 결정됨.
'INPUT': Incoming (Local-In)- local socket 으로 인입될 때 (목적지 주소가 내 장비 자신을 향하는 것. 보통은 User Application의 socket 으로 전달됨.)
- 통상 IPSecVPN 을 예로 들면 암호화된 ESP 패킷의 목적지 주소는 장비 주소 자신으로 하여 인입되고 xfrm module을 통해서 Decapsulation/Decrypt/Decompress 된 패킷은 다시 dst_input으로 회기하여 Local-In 또는 Forward가 결정됨.
- 위 그림에서 NF_XXX_LOCAL_IN 으로 표시된 부분
- local socket 으로 인입될 때 (목적지 주소가 내 장비 자신을 향하는 것. 보통은 User Application의 socket 으로 전달됨.)
'FORWARD': Forward- 라우팅되어 포워드될 때
- 위 그림에서 NF_XXX_FORWARD 으로 표시된 부분
- DEV-NOTE: Linux Kernel source 상에서 보면 통상적으로 IPv4 기준인 경우에는 dst_input이 ip_forward 함수로 결정되어 흐르는 기점을 의미함.
'OUTPUT': Outgoing (Local-Out)- local 에서 생성된 패킷을 라우팅하기 전
- 위 그림에서 NF_XXX_LOCAL_OUT 으로 표시된 부분
'POSTROUTING': post-routing- packet 이 외부로 나가려고 할 때
- 위 그림에서 NF_XXX_POST_ROUTING 으로 표시된 부분
- DEV-NOTE: Linux Kernel source 상에서 보면 통상적으로 IPv4 기준인 경우에는 dst_output 함수 호출 이후를 의미함. (dst_output은 함수 포인터로 XXX_output 함수로 분기됨. "skb_dst(skb)->output()" 형태의 호출구조)
- dst_output 함수는 다음과 같이 분기되어 다른 호출 흐름을 갖게 됨. (크게는 Unicast/Multicast/Tunnel 의 유형에 의해서 결정)
- 테이블(Table) :
'-t, --table <table>''filter'- 패킷을 허용할지 거부할지 선택하기 위한 table 입니다.
'-t <table>'옵션이 주어지지 않으면 기본적으로'-t filter'옵션이 주어졌다고 가정하게 됩니다. 즉, 'filter'는 기본 table 입니다.- 이 table 은 기본적으로 내장된 INPUT/FORWARD/OUTPUT chain이 포함됩니다.
'nat'- 주소변환을 위한 table 입니다.
- 이 table 은 기본적으로 내장된 PREROUTING/INPUT/OUTPUT/POSTROUTING chain이 포함됩니다.
- NOTE: 통상적으로 DNAT은 PREROUTING, SNAT/MASQUERADE는 POSTROUTING에서 하도록 정책을 설정하는 것이 유효합니다.
'mangle'- 패킷의 여러가지 변조를 위한 table 입니다.
- 이 table 은 기본적으로 내장된 PREROUTING/INPUT/FORWARD/OUTPUT/POSTROUTING chain이 포함됩니다.
- NOTE: Linux Kernel v2.4.17 이하 버젼에서는 PREROUTING/OUTPUT chain만 포함됩니다.
'raw'- 'NOTRACK' 대상(target)을 위한 table 입니다.
- 이 table 은 기본적으로 내장된 PREROUTING/OUTPUT chain이 포함됩니다.
'security'- 'SECMARK' 및 'CONNSECMARK' 대상에 의해 활성화된 것과 같은 MAC(Mandatory Access Control) 네트워킹 규칙을 위한 table 입니다.
- 이 table 은 기본적으로 내장된 INPUT/FORWARD/OUTPUT chain이 포함됩니다.
- 행위/액션(Action)
'-A, --append <chain> <rule-specification>': APPEND (정책 추가)'-C, --check <chain> <rule-specification>': CHECK (정책 검사)'-D, --delete <chain> <rule-specification or rulenum>': DELETE (정책 삭제)'-I, --insert <chain> [<rulenum(default:1)>] <rule-specification>': INSERT (정책 삽입)'-R, --replace <chain> <rulenum> <rule-specification>': REPLACE (정책 교체)'-L, --list [<chain>]': LIST (정책 나열)'-v, --verbose'옵션과 함께 사용하면 좀 더 자세한 정보가 나열됩니다.'-n, --numeric'옵션과 함께 사용하면 주소와 포트를 해석된 문자열이 아닌 숫자 형태로 표시합니다.'--line-numbers'옵션과 함께 사용하면 순번이 함께 표시됩니다.
'-F, --flush [<chain>]': FLUSH (모든 선택된 chain 정책 삭제)'-N, --new-chain <chain>': 새로운 chain 생성'-P, --policy <chain> <target>': POLICY (기존 정책 설정)'-E, --rename-chain <old-chain> <new-chain>': chain 변경
- 매치/일치 조건(Match)
'-m, --match <match>': 확장된 매치/일치 조건 (적절한 확장 모듈 필요)'-s, --src, --source <address>[/<mask>][,<...>]': 출발지'-d, --dst, --destination <address>[/<mask>][,<...>]': 목적지'-p, --proto <protocol>': 프로토콜'-j, --jump <target>': 매치되는 패킷을 처리하는 target'-g, --goto <chain>': 매치되는 패킷을 처리하는 chain'-i, --in-interface <name>': 인입 인터페이스'-o, --out-interface <name>': 출력 인터페이스
- 타겟/동작/대상(Target)
'ACCEPT': 허용 (패킷을 통과)'DROP': 거부 (패킷을 버림)'REJECT': 거부 및 적절한 응답 ('DROP'과 더불어서 도달하지 못한다는 적절한 응답을 출발지로 반향함,'--reject-with <reject종류>')'LOG': 로깅 ('--log-level <log-level>','--log-prefix <string>','--log-tcp-sequence','--log-tcp-options','--log-ip-options')'SNAT': 출발지 변환 ('--to <변환주소>'또는'--to-source <변환주소>')'DNAT': 목적지 변환 ('--to <변환주소>'또는'--to-destination <변환주소>')'REDIRECT': 재지향 ('--to-ports <변환할 포트>')'MASQUERADE': 출발지 변환 ('--to-ports <변환할 포트 범위>')'RETURN': 현재 chain 순회를 중지하고 이전 호출한 Chain 에서 이어서 진행
1.2. 주요 사용 예시
- 기본 Chain 확인
$ iptables -L
- 기본 Chain 상세 확인
$ iptables -v -n --line-numbers -L
- 기본 Chain 상세 확인
- 규칙에 매치되지 않은 패킷들에 대한 처리를 어떻게 할 것인지 기본 정책을 각 Chain별 명시
- INPUT CHAIN 의 기본 정책을 DROP으로 명시
$ iptables -P INPUT DROP
- INPUT Chain 의 기본 정책을 REJECT로 명시
$ iptables -P INPUT REJECT
- FORWARD Chain 의 기본 정책을 ACCEPT로 명시
$ iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
- INPUT CHAIN 의 기본 정책을 DROP으로 명시
- 인터페이스 lo 로 인입되는 모든 패킷을 허용(ACCEPT)
$ iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
- 연결상태가 ESTABLISHED(연결 상태), RELATED(연관성)인 패킷의 인입(INPUT)을 허용(ACCEPT)
$ iptables -A INPUT -m state -–state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
- 참고로 state에는 NEW, ESTABLISHED, RELATED, INVALID가 있습니다.
- 80/tcp 인입(INPUT)을 허용(ACCEPT)
$ iptables -A INPUT -p tcp –dport 80 -j ACCEPT
- 인입(INPUT)되는 패킷 중에서 목적지 192.168.0.2 로 들어오는 SSH(22/tcp) 를 차단
$ iptables -A INPUT -d 192.168.0.2 -p tcp –dport 22 -j DROP
- 내부 출발지 192.168.0.2 에서 외부로 나가는 모든 80/tcp 를 허용
$ iptables -A OUTPUT -s 192.168.0.2 -p tcp –dport 80 -j ACCEPT
- TCP에 대하여 출발지 포트변환을 1024-31000사이로 Masquerade 설정
$ iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -p TCP -j MASQUERADE --to-ports 1024-31000
- 80/tcp 목적지 포트를 8080/tcp 로 재지향
$ iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 8080
- Forward 되는 tcp 패킷에 대한 debug 로그 활성화하고 로그 앞에 'TCP-FORWARD-PACKET' 이라고 추가
$ iptables -A FORWARD -p tcp -j LOG --log-level debug --log-prefix "TCP-FORWARD-PACKET "
- 모든 체인에 정의된 모든 규칙 삭제
$ iptables -F
- INPUT Chain 의 모든 규칙 삭제
$ iptables -F INPUT
- FORWARD Chain 의 모든 규칙 삭제
$ iptables -F FORWARD
- OUTPUT Chain 의 모든 규칙 삭제
$ iptables -F OUTPUT
- INPUT Chain 의 모든 규칙 삭제
1.3. 참고 자료
- OSI 7 계층모델
- IPv4
- IPv6
- TCP(Transmission Control Protocol)
- ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol)
- NAT(Network Address Translation)
- Computing the Internet Checksum (RFC1071)
- Linux Kernel의 skbuff(Socket buffer descriptors)에 대하여
- XDP(eXpress Data Path)
- VPN(Virtual Private Network, 가상사설망)
- 우분투(Ubuntu) 가상머신(Virtual Machine) 서버 환경 구축
- VXLAN (Virtual eXtensible Local Area Network)
![[https]](https://www.minzkn.com:443/moniwiki/imgs/https.png) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iptables
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iptables![[]](/moniwiki/imgs/moni2/external.png)
![[https]](https://www.minzkn.com:443/moniwiki/imgs/https.png) https://www.netfilter.org/
https://www.netfilter.org/![[]](/moniwiki/imgs/moni2/external.png)
![[https]](https://www.minzkn.com:443/moniwiki/imgs/https.png) https://ipset.netfilter.org/iptables.man.html
https://ipset.netfilter.org/iptables.man.html![[]](/moniwiki/imgs/moni2/external.png)
![[https]](https://www.minzkn.com:443/moniwiki/imgs/https.png) https://www.linux-india.org/linux-firewall/
https://www.linux-india.org/linux-firewall/![[]](/moniwiki/imgs/moni2/external.png)
![[https]](https://www.minzkn.com:443/moniwiki/imgs/https.png) Iptables Tutorial - Oskar Andreasson
Iptables Tutorial - Oskar Andreasson![[]](/moniwiki/imgs/moni2/external.png) (https://www.frozentux.net/iptables-tutorial/chunkyhtml/index.html)
(https://www.frozentux.net/iptables-tutorial/chunkyhtml/index.html)
![[https]](https://www.minzkn.com:443/moniwiki/imgs/https.png) Acceleration of IPTABLES Linux Packet Filtering using GPGPU
Acceleration of IPTABLES Linux Packet Filtering using GPGPU![[]](/moniwiki/imgs/moni2/external.png) (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261550748_Acceleration_of_IPTABLES_Linux_Packet_Filtering_using_GPGPU)
(https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261550748_Acceleration_of_IPTABLES_Linux_Packet_Filtering_using_GPGPU)
![[https]](https://www.minzkn.com:443/moniwiki/imgs/https.png) https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/security_guide/configuring_complex_firewall_rules_with_the_rich-language_syntax
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/security_guide/configuring_complex_firewall_rules_with_the_rich-language_syntax![[]](/moniwiki/imgs/moni2/external.png)
![[https]](https://www.minzkn.com:443/moniwiki/imgs/https.png) https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/configuring_and_managing_networking/using-and-configuring-firewalld_configuring-and-managing-networking
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/html/configuring_and_managing_networking/using-and-configuring-firewalld_configuring-and-managing-networking![[]](/moniwiki/imgs/moni2/external.png)
![[https]](https://www.minzkn.com:443/moniwiki/imgs/https.png) https://stuffphilwrites.com/2014/09/iptables-processing-flowchart/
https://stuffphilwrites.com/2014/09/iptables-processing-flowchart/![[]](/moniwiki/imgs/moni2/external.png) : iptables Processing Flowchart (Updated Often)
: iptables Processing Flowchart (Updated Often)
| 참고 영상 |
| 참고 영상 |
| 참고 영상 |